Trump’s Second Term May Bring Unexpected Tax Changes — Here’s What You Need To Know – Financial Freedom Countdown

With former President Donald Trump reclaiming the White House after defeating Vice President Kamala Harris, taxpayers could soon experience the impact of his bold tax agenda.
Trump’s 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) brought sweeping changes, including lower tax brackets, a higher standard deduction, and an expanded child tax credit. During his campaign, he hinted at even more dramatic cuts, such as eliminating taxes on Social Security benefits and tips and further reducing corporate tax rates.
One of the most significant moves on the horizon could be the extension of key provisions from the TCJA, which are set to expire in 2025.
Here’s a look at the TCJA provisions that may sunset next year without Congressional action.
Individual Tax Rates Lowered

The TCJA revised the tax structure by reducing tax rates across various income brackets and modifying the income ranges associated with each tax bracket.
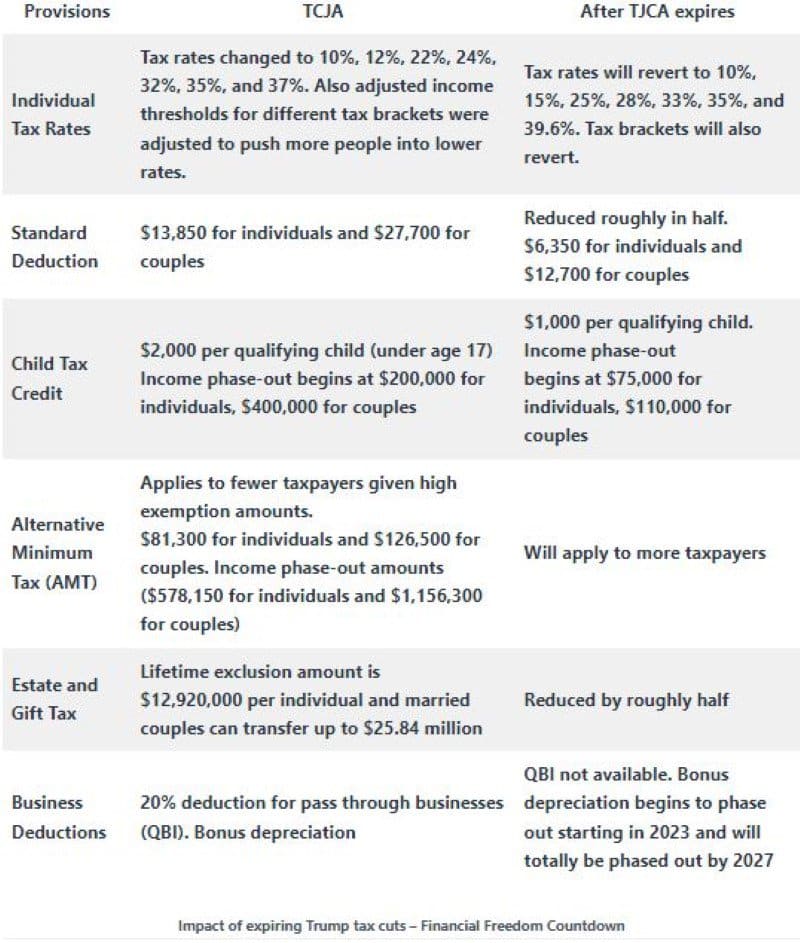
Previously, there were seven tax brackets with respective rates of 10%, 15%, 25%, 28%, 33%, 35%, and 39.6%.
Under the TCJA, these were adjusted to rates of 10%, 12%, 22%, 24%, 32%, 35%, and 37%, resulting in a reduction of taxes for the majority of taxpayers.
Standard Deduction Doubled

The standard deduction was nearly doubled under the TCJA. It increased from $13,000 to $24,000 for joint filers and $6,500 to $12,000 for individuals.
Higher Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) Exemption Amounts

The TCJA also changed how the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) is calculated, so it applied to only high-income individuals. It now only affects fewer people due to more significant exemption amounts ($81,300 for individuals and $126,500 for couples).
However, after the TCJA expires, more people might have to pay it again because the exemption amounts and income phase-out thresholds will decrease.
Child Tax Credit Doubled

The TCJA doubled the child tax credit from $1,000 to $2,000 per child. Currently, you can get this credit for each child under 17, and it starts to phase out if you make more than $200,000 as an individual or $400,000 as a couple.
After the TCJA expires, the child tax credit will decrease to $1,000 per qualifying child, and it will start to phase out if you make more than $75,000 as an individual or $110,000 as a couple.
Retirement Planning

When the TCJA expires, the tax brackets will go back to what they were before, which means some people might have to pay more in taxes since the top tax bracket will increase from the current 37% to 39.6%.
Given this situation, it would be prudent to explore avenues for pulling income forward within the next few years to leverage the current lower brackets. You can do this by exercising stock options now and avoiding deferred compensation plans.
Traditional IRAs require minimum distributions (RMDs) commencing at age 73 and are taxable as ordinary income. On the other hand, Roth IRAs do not impose RMDs, and all future growth and distributions remain exempt from taxation.
One of the benefits of early retirement is that taxpayers have several years between their retirement date and RMD age to convert their IRAs to Roth IRAs in a lower tax bracket.
If you are not planning for early retirement and your income is expected to continue to increase over the next couple of years, by converting your traditional IRA to a Roth IRA before 2026, you would assume the upfront income tax liability (potentially at a lower tax rate), rather than facing it at the time of distribution.
The SECURE Act eliminated the Stretch IRA provisions. For individuals who are subject to the 10-year rule on inherited IRAs, it is advisable to contemplate the possibility of opting for more substantial distributions before the expiration of the TCJA, especially if there is concern regarding the potential rise in tax rates during the later stages of the mandatory 10-year window for complete distribution of the account.
Capital Gains Tax

With stock markets at record highs, investing in stocks has resulted in a lot of unrealized capital gains.
With the TJCA, the tax brackets for long-term capital gains and qualified dividends are not linked to the ordinary income tax brackets.
Check with your tax advisor on selling some of your stocks if you anticipate potentially higher future tax rates.
You could maximize Long Term Capital Gains while in the lower bracket for your marginal rate and harvesting losses to offset gains when appropriate.
Lifetime Gift and Estate Tax Exemption Doubled

The TCJA doubled the lifetime gift and estate tax exemption limits.
As of 2023, individuals are eligible to transfer up to $12.92 million, while married couples can transfer up to $25.84 million without incurring federal gift taxes or estate taxes, either during their lifetime or as part of their estate.
This historically high exemption amount will be halved after the 2025 tax year.
Check with your tax advisor if it is worth accelerating those gifting plans to your children and grandchildren each year. For those with even larger estates, it is time to consider possible larger lifetime gifts.
Tax strategy should be a key consideration when setting up living trusts.
Business Deductions

The TCJA introduced qualified business income (QBI) deduction, facilitating pass-through businesses to deduct a maximum of 20 percent of their earnings. Notice 2019-07 introduced a new safe harbor provision for rental real estate under Section 199A of the Internal Revenue Code, making rental properties eligible for QBI.
Under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), the qualification for 100% bonus depreciation was introduced depending on the year you placed the assets into service. For real estate investing, many interior upgrades to buildings are eligible for purposes of bonus depreciation. Utilizing a cost segregation study is one of the methods to ensure eligibility for the available bonus depreciation percentage.
Current provisions allow for a quicker depreciation of certain assets, which is a boon for reducing taxable income. However, post-sunset, the elongation of this timeline could mean higher taxable income. Check with your tax advisor for capitalizing on the existing provisions by accelerating depreciation to lower your taxable bracket.
What Happens if Trump Tax Cuts Expire in 2025?
If the TCJA is not extended, a number of tax provisions would expire.
Elimination of Cap on SALT Deductions in TJCA

As part of the TCJA, state and local tax (SALT) deductions were capped at $10,000. Residents of high tax states such as California, Illinois and New York were unable to have unlimited local and state taxes deducted on their Federal tax returns.
Some of the tax proposals call for eliminating the limit on SALT deductions.
Trump’s ‘No Tax on Tips’ Plan

Trump’s promise to eliminate taxes on tips could impact the roughly 2.5% of workers who rely on tips for their income and was received quite well during the campaign. In fact, Kamala Harris adopted the same slogan a few days later.
Although the policy has a nice ring to it, the ripple effects might go much further. If more industries shift to a tipping-based model with workers earning a base wage and the rest of their income from tax-free tips, even white-collar jobs could see a portion of salaries reclassified as tips.
While this approach could lighten workers’ tax burdens, it risks creating chaos in pay structures, confusing consumers, and slashing the government’s income tax revenue.
Removing Taxes on Overtime Pay

Trump also mentioned removing taxes on overtime pay

Trump has proposed making Social Security income tax-free for seniors.
Currently, around 40% of Social Security recipients pay federal income taxes, usually because other income sources push them above a certain threshold.
Lowering Corporate Tax

The current corporate income tax rate stands at a flat 21%.
Trump has proposed reducing it to 20% or even 15% for corporations that manufacture their products within the United States.
Tax Cuts Paid by Tariffs

Eliminating these taxes would reduce federal tax revenue, potentially increasing the deficit or leading to cuts in other areas to balance the shortfall..
At present, the U.S. levies an average tariff of just 2% on imported industrial goods.
Trump has previously suggested implementing a universal tariff of 10-20% on all imports and a steep 60% tariff specifically targeting imports from China.
Hope for Implementing all Tax Breaks Looks Bleak

Animosity between the parties is high after a grueling election season. These plans will face scrutiny as Republicans, despite holding a majority in the House and Senate, must weigh the fiscal impact of another round of tax cuts—setting up a tense debate that could define Trump’s second term.
As the TCJA provisions edge closer to their expiration date of 2025, individuals must remain proactive in their tax planning efforts. It is crucial to reassess your investment strategy and explore opportunities to take advantage of the current tax provisions.
Tax planning can be complex, especially when dealing with changing tax laws. Seek guidance from a licensed tax professional to ensure your financial goals align with the evolving tax landscape.
Like this content? Follow Financial Freedom Countdown
Retire Abroad and Still Collect Social Security? Avoid These 9 Countries Where It’s Not Possible

Dreaming of retiring to a sun-drenched beach or a quaint village? Many Americans envision spending their golden years abroad, savoring the delights of new cultures and landscapes. However, an essential part of this dream hinges on the financial stability provided by Social Security benefits. Before packing your bags and bidding farewell, it’s crucial to know that not all countries play by the same rules when it comes to collecting these benefits overseas. Here are the nine countries where your dream of retiring abroad could hit a snag, as Social Security benefits don’t cross every border. Avoid living in these countries so your retirement plans don’t get lost in translation.
Retire Abroad and Still Collect Social Security? Avoid These 9 Countries Where It’s Not Possible
Shift From Employee to Investor Mindset with the Cashflow Quadrant Methodology by Robert Kiyosaki

Countless systems have been established that provide a much better understanding of what income generation is, how it can be used, and how individuals can organize their financial life as they work towards financial freedom. One of the more successful and better-known examples of financial education is the Cashflow Quadrant, the book by Robert Kiyosaki. Rich Dad’s Cashflow Quadrant was revolutionary for the way it organized money and helped people better learn how to increase their income. As the name implies, there are four quadrants within the Cashflow Quadrant. By mastering each of the four categories – or specializing in one – a person can increase their revenue stream and ultimately make more money.
Shift From Employee to Investor Mindset with the Cashflow Quadrant Methodology by Robert Kiyosaki
AARP Survey Reveals Over 50% of Americans 50 and Older Fear Financial Ruin in Retirement

A recent AARP survey highlights a dire situation for older Americans: 20% of adults aged 50 and above have no retirement savings at all. This lack of financial preparedness is causing significant anxiety, with 61% of this age group worried they won’t have enough money to support themselves in retirement.
AARP Survey Reveals Over 50% of Americans 50 and Older Fear Financial Ruin in Retirement

Choosing when to claim Social Security is a crucial decision for retirees. The two main options are claiming benefits at 62 to conserve retirement savings or using 401(k) funds to delay Social Security until 70. Both strategies come with pros and cons, depending on your financial needs and long-term goals.
Is Tapping Your 401(k) to Delay Social Security Until 70 a Risky Move for Your Retirement?
Retirement Expectations Clash with Reality as Social Security’s Future Remains Uncertain

As economic concerns continue to grow, a significant disconnect persists between how non-retirees perceive their future financial stability and the actual experience of current retirees, particularly with respect to Social Security.
Retirement Expectations Clash with Reality as Social Security’s Future Remains Uncertain

The official Social Security cost-of-living adjustment (COLA) numbers released on 10th October are a disappointing 2.5%, a sharp drop from the 3.2% increase retirees received in 2024. Next year’s COLA falls far short of the 8.7% adjustment for 2023, which was the largest increase in over 40 years and meant to help seniors and people with disabilities keep up with soaring prices. This meager adjustment raises concerns about how seniors will cope with persistent inflation
2025 Social Security COLA Forecast Disappoints Retirees Struggling to Keep Up with Soaring Inflation

The Social Security system is undergoing significant changes starting in 2025, with updates poised to affect beneficiaries and workers nationwide. From reduced Cost of Living Adjustments (COLAs) to increased Medicare premiums and tax thresholds, these changes are a response to shifting economic and demographic trends. It’s crucial to understand how these adjustments will impact you.
Social Security Shake-Up: Key Changes Coming in 2025 That Could Impact Your Benefits
Did you find this article helpful? We’d love to hear your thoughts! Leave a comment with the box on the left-hand side of the screen and share your thoughts.
Also, do you want to stay up-to-date on our latest content?
1. Follow us by clicking the [+ Follow] button above,
2. Give the article a Thumbs Up on the top-left side of the screen.
3. And lastly, if you think this information would benefit your friends and family, don’t hesitate to share it with them!

John Dealbreuin came from a third world country to the US with only $1,000 not knowing anyone; guided by an immigrant dream. In 12 years, he achieved his retirement number.
He started Financial Freedom Countdown to help everyone think differently about their financial challenges and live their best lives. John resides in the San Francisco Bay Area enjoying nature trails and weight training.
Here are his recommended tools
Personal Capital: This is a free tool John uses to track his net worth on a regular basis and as a retirement planner. It also alerts him wrt hidden fees and has a budget tracker included.
Platforms like Yieldstreet provide investment options in art, legal, real estate, structured notes, venture capital, etc. They also have fixed-income portfolios spread across multiple asset classes with a single investment with low minimums of $10,000.




